I. The background
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), also called sexually transmitted infection (STIs), is a class of infection caused by microorganisms mainly spread through sexual contact (vaginal, anal and oral sex). There are more than 30 pathogens that could conduct STIs, which are including bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites.
STIs is very common all over the world. More than 1 million cases of curable STIs new infected happens each day. There are 36.3 million people with HIV, 417 million people with HSV-2 and 291 million people with HPV in the globe. The WHO estimates that there are more than 2.3 million deaths caused by STIs each year, which are including HIV, hepatitis, syphilis, cervical cancer caused by HPV.
Figure 1. New cases of four curable STIs among adults (15–49 years old)
per year, by sex, global, 2020
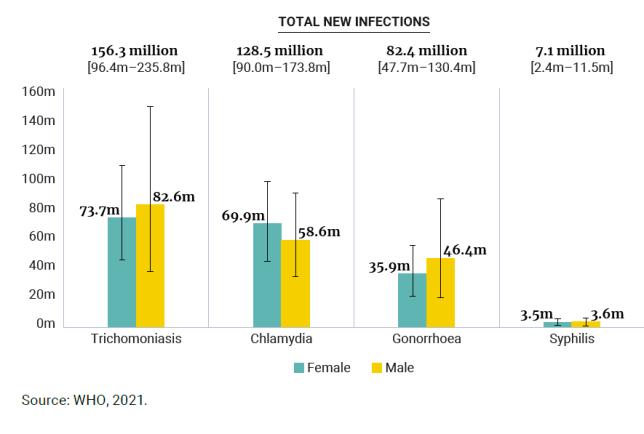
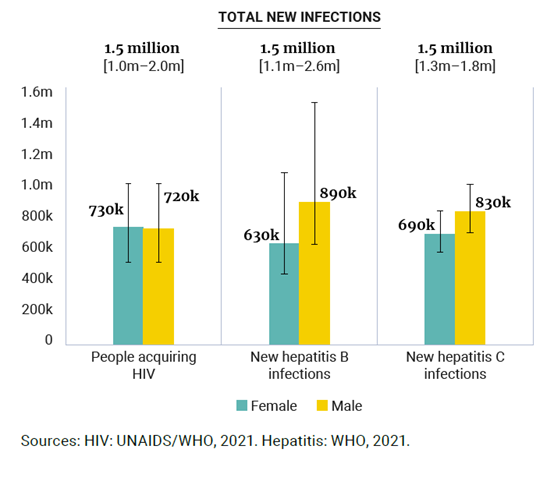
Figure 2. New cases of HIV, hepatitis B infection and hepatitis C virus
infection per year, by sex, global, 2019–2020
Experienced decades of development, the technology of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) has become common in the detection of microorganism. It supplies a tool of evidence-base-decision in both of diagnosis of asymptomatic and symptomatic infections. The PCR tests has been widely used in high-income and middle-income countries. Using accurate diagnostic tests could effectively prevent and reduce the prevalence and transmission of STIs on early stage. The CDC and WHO have recommenced using molecular method to accurate diagnostic tests and screening strategies.
II. Guidelines for the management of symptomatic STIs issued by WHO
For minimizing the transmission of STIs and reducing incidence of STIs, WHO published a new guideline to manage STIs patients with clinical symptoms in July, 2021. It aims to improve the quality of managing symptomatic STIs by providing evidence-informed recommendations.
The objectives of these guidelines are:
• to provide updated, evidence-informed clinical and practical recommendations on the case
management of people with symptoms of STIs;
• to support countries in updating their national guidelines for the case management of people
with symptoms of STIs.
The guidelines provide recommended 5 managements of symptomatic infections, including:
• urethral discharge syndrome, including persistent urethral discharge syndrome;
• vaginal discharge syndrome, including persistent vaginal discharge;
• anorectal infection;
• genital ulcer disease syndrome;
• lower abdominal pain syndrome.
The CDC and WHO have recommenced using molecular method to accurate diagnostic tests and screening strategies. [CDC,2015; WHO, 2016]
To summarize, the main recommendations for symptomatic management including;
- Treatment based on molecular diagnosis is prior recommended for all of 5 conditions.
- Taking syndromic treatment should be taken based on clinical symptoms, sexual history (or other infectious chances) and physical examination on the same day of visit when limited or unavailable molecular tests.
- Taking specific treatment and management based on certainty evidence from molecular tests or other lab tests when molecular testing results available on the same-day.
- Taking syndromically treatment based on clinical conditions of lab results unavailable in the same day of visit. The test results can support to managing the partners. Other tests may supply a basic evidence, such as rapid tests. For people with recurrent or persistent STIs, a molecular diagnosis can be helpful for further treatment.
- WHO recommends that, for effective prevention and control STIs, the whole diagnostic process (including from sampling to results output) should be shorten as possible and the testing results should be provided on the same day.
- In addition, The STIs usually conducts serious consequences for human health. To using best diagnostic tests is effective way to reduce morbidity. WHO suggests to establish quality-assured laboratory based standard quality management system. A quality-assured molecular testing laboratory with a fully operational management system can provide reliable, sensitive, specific results.
Available molecular detection in laboratory diagnosis
|
Urethral discharge syndrome
|
|
NAAT is the current gold standard for detecting C. trachomatis and N. gonorrhoeae among
men and women.
Used to detect:
- N. Gonorrhoeae (urine or a urethral swab)
- C. Trachomatis (urine or a urethral swab)
- M. Genitalium (a first-catch urine in men)
- T. Vaginalis (urine)
|
|
Vaginal discharge syndrome
|
|
NAAT has the highest sensitivity of all diagnostic methods to detect T. vaginalis.
NAAT is gold standard technology for detection of C. trachomatis and N. gonorrhoeae among both symptomatic and asymptomatic women.
Samples from vaginal swabs (first choice), endocervical swabs, urine.
- T. vaginalis
- C. albicans
- C. trachomatis
- N. gonorrhoeae
|
|
Genital ulcer disease syndrome
|
|
Amplified molecular detection by PCR of HSV DNA from swabs of genital lesions is the most
sensitive and specific test. Using a combined HSV and T. pallidum PCR, when available, would be of added benefit to implicate or exclude syphilis at the same time. PCR assays have also been developed for HSV-1 and HSV-2.
- HSV-1
- HSV-2
- T. pallidum
- H. ducreyi
|
III. Devoting to molecular diagnostic solution for women’s health
Specialized in developing affordable real-time PCR kits with highly sensitivity and specificity for STIs. Bioperfectus has so far launched 4 products to protect and improve women’s health.
*Neisseria Gonorrhoeae Real Time PCR Kit>>
*Ureaplasma Urealyticum Real Time PCR Kit>>
*Neisseria Gonorrhoeae/Chlamydia Trachomatis/U. Urealyticum Real Time PCR Kit>>
Reference list
"Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) fact sheet." N.p, n.d. Web. 26 Jul. 2021 <https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/sexually-transmitted-infections-(stis)>.
"Guidelines for the management of symptomatic sexually transmitted .." N.p, n.d. Web. 26 Jul. 2021 <https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/9789240024168>..
"Global progress report on HIV, viral hepatitis and sexually .." N.p, n.d. Web. 26 Jul. 2021 <https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/9789240027077>.
"Sexually Transmitted Diseases - Information from CDC." N.p, n.d. Web. 26 Jul. 2021 <https://www.cdc.gov/std/default.htm>.

